第 3 章 接口与 API 设计
第 15 条:用前缀避免命名空间冲突
- Objectice-C 没有其他语言那种内置的命名空间(namespace)机制,很容易产生重名问题。
- 避免命名冲突(naming clash)的唯一办法就是变相实现命名空间:为所有名称都加上适当的前缀。
- 前缀可以是与公司、应用程序或二者皆有关联之名。
- 前缀应该是三个字母的。两字母前缀是 Apple 保留使用的。
- 不仅是类名,应用程序中的所有名称都应该加前缀。
- ⚠️ 类实现文件中所用的纯 C 函数及全局变量在编译好的目标文件中算作顶级符号,也应加上前缀。
要点
- 选择与你公司、应用程序或者二者皆有关联之名称作为类名的前缀,并在所有代码中均使用这一前缀。
- 若自己所开发的程序库中用到了第三方库,则应为其中的名称加上前缀。
- Apple 宣称保留使用所有两字母前缀的权利,所以自己所选用的前缀最好是三字母的。
第 16 条:提供 “全能初始化方法”
全能初始化方法 \ 指定初始化方法:为对象提供必要信息以便其能完成工作的初始化方法。
我更倾向于把它称之为 指定初始化方法。
示例:
矩形类
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface EOCRectangle : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float width;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float height;
- (instancetype)initWithWidth:(float)width
andHeight:(float)height;
@end
#import "EOCRectangle.h"
@implementation EOCRectangle
// ✏️ 指定初始化方法
- (instancetype)initWithWidth:(float)width
andHeight:(float)height {
// ✏️ 调用超类的指定初始化方法,以维持调用链
if (self = [super init]) {
_width = width;
_height = height;
}
return self;
}
// ✏️ 覆写非指定初始化方法
// 1.使用默认值
- (instancetype)init {
return [self initWithWidth:5.0f andHeight:10.0f];
}
// 2.抛出异常
//- (instancetype)init {
// @throw [NSException exceptionWithName:NSInternalInconsistencyException
// reason:@"Use designated Initizlizer Method"
// userInfo:nil];
// return nil;
//}
@end正方形类
#import "EOCRectangle.h"
@interface EOCSqure : EOCRectangle
- (instancetype)initWithDimension:(float)dimension;
@end
#import "EOCSqure.h"
@implementation EOCSqure
// ✏️ 【指定初始化方法】要调用【超类的指定初始化方法】
- (instancetype)initWithDimension:(float)dimension {
return [super initWithWidth:dimension andHeight:dimension];
}
// ✏️ 【子类的指定初始化方法】与【超类的指定初始化方法】不一致时,应该覆写【超类的指定初始化方法】
- (instancetype)initWithWidth:(float)width andHeight:(float)height {
float dimension = MAX(width, height);
return [self initWithDimension:dimension];
}
@end编写多个指定初始化方法的情况:
NSCoding 协议
// EOCRectangle.m
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder {
// ✏️ 先调用超类的相关方法,再执行与本类有关的任务
if (self = [super init]) {
_width = [aDecoder decodeFloatForKey:@"width"];
_height = [aDecoder decodeFloatForKey:@"height"];
}
return self;
}
// EOCSqure.m
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder {
// ✏️ 因为超类 EOCRectangle 也实现了 NSCoding 协议,所以这里调用超类的 initWithCoder: 初始化方法
if (self = [super initWithCoder:aDecoder]) {
// EOCSquare's specific initializer
}
return self;
}要点
- 在类中提供一个全能初始化方法,并于文档里指明。其它初始化方法均应调用此方法。
- 若全能初始化方法与超类不同,则需覆写超类中对应方法。
- 如果超类的初始化方法并不适用于子类,那么应该覆写这个超类方法,并在其中抛出异常。
第 17 条:实现 description 方法
- NSObject 类中默认的实现,输出类名和对象的内存地址。
覆写 description 方法一:
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p,\"%@ %@\">",[self class], self, _firstName, _lastName];
}效果:
EOCPerson *person = [[EOCPerson alloc] init];
person.firstName = @"Chester";
person.lastName = @"Bennington";
NSLog(@"person = %@",person);
// Output:
// person = <EOCPerson: 0x100303030,"Chester Bennington">方法二:借助 NSDictionary 类
在自定义的 description 方法中,把待打印的信息放到字典里面,然后将字典对象的 description 方法所输出的内容包含在字符串里返回。
简而言之,就是把对象需要打印的属性封装在 NSDictionary 中。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
/**
坐标类
*/
@interface EOCLocation : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float latitude;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float longtitude;
- (instancetype)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title
latitude:(float)latitude
longtitude:(float)longtitude;
@end
#import "EOCLocation.h"
@implementation EOCLocation
- (instancetype)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title
latitude:(float)latitude
longtitude:(float)longtitude {
if (self = [super init]) {
_title = [title copy];
_latitude = latitude;
_longtitude = longtitude;
}
return self;
}
// ✏️ 把对象需要打印的属性封装在 NSDictionary 中
- (NSString *)description {
NSDictionary *dictionary = @{
@"title" :_title,
@"latitude" :@(_latitude),
@"longtitude" :@(_longtitude),
};
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p,%@>",[self class], self, dictionary];
}
@end效果:
location = <EOCLocation: 0x100203ef0,{
latitude = "120.51";
longtitude = "30.4";
title = ShangHai;
}>方法三:借助 YYModel 框架 yy_modelDescription 方法
-(NSString *)description {
return [self yy_modelDescription];
}效果:
location = <EOCLocation: 0x100300190> {
latitude = 120.51;
longtitude = 30.4;
title = "ShangHai"
}debugDescription 方法
debugDescription方法是开发者在调试器(debugger)中以控制台命令打印对象时才调用的。- 在 NSObject 类的默认实现中,此方法只是直接调用了
description方法。
// 普通描述信息
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@",_firstName, _lastName];
}
// 调试时使用详细的描述信息
- (NSString *)debugDescription {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p,\"%@> %@\">",[self class], self, _firstName, _lastName];
}要点
- 实现
description方法返回一个有意义的字符串,用以描述该实例。 - 若想在调试时打印出更详尽的对象描述信息,则应该实现
debugDescription方法。
第 18 条:尽量使用不可变对象
- 设计类时,应该充分运用属性(
@property)来封装数据(参见第 6 条)。 - 不必要对外公开的属性可以放在分类(class-continuation)中。
- 应该尽量把对外公布出来的属性设置为只读(
readonly),而且只在确有必要时才将属性对外公布。 - 如果想修改封装在对象内部的数据,但是却不想另这些数据为外人所改动,我们可以在对象内部分类(class-continuation)中将
readonly属性重新声明为readwrite。
// EOCLocation.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
/**
坐标类
*/
@interface EOCLocation : NSObject
// ✏️ 对外设置为 readonly
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *identifier;
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float latitude;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) float longtitude;
- (instancetype)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier
Title:(NSString *)title
latitude:(float)latitude
longtitude:(float)longtitude;
@end
// EOCLocation.m
#import "EOCLocation.h"
#import "YYModel.h"
@interface EOCLocation ()
// ✏️ 内部重新设置为 readwrite
@property (nonatomic, copy, readwrite) NSString *identifier;
@property (nonatomic, copy, readwrite) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readwrite) float latitude;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readwrite) float longtitude;
@end
@implementation EOCLocation
- (instancetype)initWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier
Title:(NSString *)title
latitude:(float)latitude
longtitude:(float)longtitude; {
if (self = [super init]) {
_identifier = [identifier copy];
_title = [title copy];
_latitude = latitude;
_longtitude = longtitude;
}
return self;
}
-(NSString *)description {
return [self yy_modelDescription];
}
@end- 对于 collection 类来说,你可以提供一个
readonly属性供外界使用,然后在内部设置一个 mutable 类型的可变集合,外界需要读取此属性的值时,就拷贝一份不可变数据给它。
// EOCPerson.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface EOCPerson : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *lastName;
// ✏️ 对外使用 NSSet
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSSet *friends;
- (instancetype)initWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName
andLastName:(NSString *)lastName;
- (void)addFirend:(EOCPerson *)person;
- (void)removeFriend:(EOCPerson *)person;
@end
// EOCPerson.m
#import "EOCPerson.h"
@implementation EOCPerson {
// ✏️ 类的内部使用 NSMutableSet
NSMutableSet *_internalFriends;
}
- (instancetype)initWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName
andLastName:(NSString *)lastName {
if (self = [super init]) {
_firstName = [firstName copy];
_lastName = [lastName copy];
_internalFriends = [NSMutableSet new];
}
return self;
}
- (void)addFirend:(EOCPerson *)person {
[_internalFriends addObject:person];
}
- (void)removeFriend:(EOCPerson *)person {
[_internalFriends removeObject:person];
}
// ✏️ 访问 NSSet 时,提供 NSMutableSet 的深拷贝不可变对象
- (NSSet *)friends {
return [_internalFriends copy];
}
@end要点
- 尽量创建不可变的对象。
- 若某属性仅可于对象内部修改,则在 “class-continuation 分类” 中将其由
readonly属性扩展为readwrite属性。 - 不要把可变的 collection 作为属性公开,而应提供相关方法,一次修改对象中的可变 collection。
第 19 条:使用清晰而协调的命名方式
- 类、方法及变量名称中一般都带有 in、for、with 等介词。
- 优点:代码读起来像日常语言里的句子,表述清晰。
- 方法与变量名使用了 “驼峰式大小写命名法”(camel casing)—— 以小写字母开头,其后每个单词首字母大写。
- 类名也用驼峰命名法,其首字母应大写,而且前面通常还有三个前缀字母。
- 方法命名应该能准确传达其所执行的任务,言简意赅。
方法命名规则
如果方法的返回值是新创建的,那么方法名的首个词应是返回值的类型,除非前面还有修饰语,例如
localizedString。 属性的存取方法不遵循这种命名方式,因为一般认为这些方法不会创建新对象,即便有时返回内部对象的一份拷贝,我们也认为那相当于原有的对象。这些存取方法应该按照其所对应的属性来命名。<!–hexoPostRenderEscape:
+ (instancetype)string;
- (instancetype)stringWithString:(NSString *)string;
(instancetype)localizedStringWithFormat:(NSString *)format, … ;:hexoPostRenderEscape–>
应该把表示参数类型的名词放在参数前面。
<!–hexoPostRenderEscape:
- (NSUInteger)lengthOfBytesUsingEncoding:(NSStringEncoding)enc;
(void)getCharacters:(unichar *)buffer range:(NSRange)range;:hexoPostRenderEscape–>
如果方法要在当前对象上执行操作。那么就应该包含动词;若执行操作时还需要参数,则应该在动词后面加上一个或多个名词。
<!–hexoPostRenderEscape:
- (NSString *)uppercaseStringWithLocale:(nullable NSLocale *)locale NS_AVAILABLE(10_8, 6_0);
(NSString *)lowercaseStringWithLocale:(nullable NSLocale *)locale NS_AVAILABLE(10_8, 6_0);:hexoPostRenderEscape–>
不要使用 str 这种简称。应该用 string 这样的全称。
Boolean 属性应加 is 前綴。如果某方法返回非属性的 Boolean 值,那么应该根据其功能,选用 has 或 is 当前缀。
<!–hexoPostRenderEscape:
- (BOOL)isEqualToString:(NSString *)aString;
- (BOOL)hasPrefix:(NSString *)str;
(BOOL)hasSuffix:(NSString *)str;:hexoPostRenderEscape–>
将 get 这个前缀留给那些借由 “输出参数” 来保存返回值的方法。比如说,把返回值填充到 “c 语言式数组”(c-style array) 里的那种方法就可以使用这个词做前缀。
<!–hexoPostRenderEscape:
- (void)getCharacters:(unichar *)buffer range:(NSRange)range;
- (BOOL)getCString:(char *)buffer maxLength:(NSUInteger)maxBufferCount encoding:(NSStringEncoding)encoding;
(void)getLineStart:(nullable NSUInteger *)startPtr end:(nullable NSUInteger *)lineEndPtr contentsEnd:(nullable NSUInteger *)contentsEndPtr forRange:(NSRange)range;:hexoPostRenderEscape–>
类与协议的命名
- 应该为类与协议的名称加上前缀,以避免命名空间冲突。
- UIKit 示例:UIView、UIViewController、UITableView、UITableViewController、UITableViewDelegate、
- 命名的方式应该协调一致。
要点
- 起名时应遵从标准的 Objective-C 命名规范,这样创建出来的接口更容易为开发者所理解。
- 方法名要言简意赅,从左至右读起来要像个日常用语中的句子才好。
- 方法名里不要使用缩略后的类型名称。
- 给方法起名时的第一要务就是确保其风格与你自己的代码或所要集成的框架相符。
第 20 条:为私有方法名加前缀
原因:
- 为私有方法名加上前缀有助于调试,因为据此很容易就能把公共方法和私有方法区别开。
- 便于修改方法名或方法签名。公共方法名不应轻易改动,而内部方法可以随意改动。
// EOCObject.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface EOCObject : NSObject
- (void)publicMethod;
@end
// EOCObject.m
#import "EOCObject.h"
@implementation EOCObject
- (void)publicMethod {
/*^.^>*/
}
- (void)p_privateMethod {
/*^.^*/
}
@end⚠️ 苹果公司喜欢单用一个下划线作私有方法的前缀。因此,开发者不应该单用一个下划线做前缀,以免无意间覆写了父类的同名方法。
要点
- 给私有方法的名称加上前缀,这样可以很容易的将其同公共方法区分开。
- 不要单用一个下划线做私有方法的前缀,因为这种做法是预留给苹果公司用的。
第 21 条:理解 Objectice-C 错误模型
- 自动引用计数(Automatic Reference Counting,ARC)在默认情况下不是 “异常安全的”(exception safe)。如果抛出异常,那么本应在作用域末尾释放的对象将不会自动释放。
- 如果想生成 “异常安全” 的代码,可以通过编译器设置
-fobjc-arc-exceptions来实现,不过这将引入一些额外的代码,即使在不抛出异常时,也照样要执行这部分(额外的)代码。 - 即使不用 ARC,也很难写出在抛出异常时不会导致内存泄漏的代码。
- Objectice-C 语言现在所采用的办法是:只在及其罕见的情况下抛出异常,异常抛出后,无须考虑恢复问题,而且应用程序此时也应该退出。
- 异常只用于处理严重错误(fatal error,致命错误)。
- 出现 “不那么严重的错误”(nonfatal error,非致命错误)时,Objectice-C 语言所用的编程范式为:令方法返回 nil/0,或是使用 NSError,以表明其中有错误发生。
NSError
NSError 对象里封装了三条信息:
- Error domain(错误范围,其类型为字符串);
- Error code (错误码,其类型为整数);
- User info (用户信息,其类型为字典)。
NSError 的第一种常见用法是通过委托协议来传递错误。
另一种用法是经由方法的 “输出参数” 返回给调用者。
- (BOOL)doSomething:(NSError **)error,传递给方法的参数是个指针,而该指针本身又指向另一个指针,那个指针指向 NSError 对象。
NSError *error = nil;
BOOL ret = [self doSomething:&error];
if (error) {
// There was an error
}最好能为你自己的程序库中所发生的错误指定一个专用的 “错误范围” 字符串。用枚举类型来表示错误码。
要点
- 只有发生了可使整个应用程序崩溃的严重错误时,才使用异常。
- 在错误不那么严重的情况下,可以指派 “委托方法”(delegate method) 来处理错误,也可把错误信息放在 NSError 对象里,经由 “输出参数” 返回给调用者。
第 22 条:理解 NSCopying 协议
如果想使某个类支持拷贝功能,需要声明该类遵从 NSCopying 协议,并实现 NSCopying 协议中的方法。
// 不可变版本
@protocol NSCopying
- (id)copyWithZone:(nullable NSZone *)zone;
@end
// 可变版本
@protocol NSMutableCopying
- (id)mutableCopyWithZone:(nullable NSZone *)zone;
@end示例:
// EOCPerson.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface EOCPerson : NSObject <NSCopying>
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, copy, readonly) NSString *lastName;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSSet *friends;
- (instancetype)initWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName
andLastName:(NSString *)lastName;
- (void)addFirend:(EOCPerson *)person;
- (void)removeFriend:(EOCPerson *)person;
@end
// EOCPerson.m
#import "EOCPerson.h"
static const NSTimeInterval KAnimationDuration = 0.3;
@implementation EOCPerson {
NSMutableSet *_internalFriends;
}
- (instancetype)initWithFirstName:(NSString *)firstName
andLastName:(NSString *)lastName {
if (self = [super init]) {
_firstName = [firstName copy];
_lastName = [lastName copy];
_internalFriends = [NSMutableSet new];
}
return self;
}
- (void)addFirend:(EOCPerson *)person {
[_internalFriends addObject:person];
}
- (void)removeFriend:(EOCPerson *)person {
[_internalFriends removeObject:person];
}
- (NSSet *)friends {
return [_internalFriends copy];
}
#pragma mark - NSCopying
// ✏️ 实现 NSCopying 协议
- (id)copyWithZone:(nullable NSZone *)zone {
// 使用指定初始化方法初始化待拷贝对象
EOCPerson *copy = [[[self class] allocWithZone:zone] initWithFirstName:_firstName andLastName:_lastName];
// 拷贝内部实例变量:1.浅拷贝
copy->_internalFriends = [_internalFriends mutableCopy];
// 拷贝内部实例变量:2.深拷贝
copy->_internalFriends = [[NSMutableSet alloc] initWithSet:_internalFriends
copyItems:YES];
return copy;
}
@end 在可变对象上调用
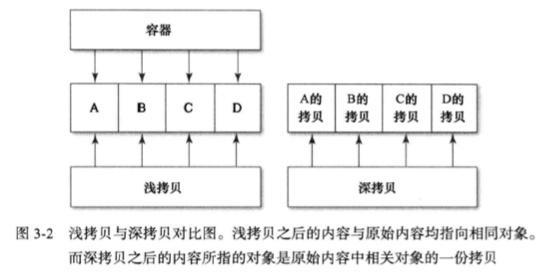
copy方法会返回另外一个不可变类的实例。深拷贝(deep copy) & 浅拷贝(shallow copy)的问题:
深拷贝:在拷贝对象自身时,将其底层数据也一并复制过去。
- (instancetype)initWithSet:(NSSet<ObjectType> *)set copyItems:(BOOL)flag;浅拷贝:只拷贝容器对象本身,而不复制其中数据。(Foundation 框架中的所有 collection 类在默认情况下都执行浅拷贝)
![]()
YYModel
该框架中有一个实现 NSCopying 协议的便捷方法:
- (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone {
return [self yy_modelCopy];
}要点
- 若想令自己所写的对象具有拷贝功能,则需实现 NSCopying 协议。
- 如果自定义的对象分为可变版本与不可变版本,那么就要同时实现 NSCopying 与 NSMutableCopying 协议。
- 复制对象时需决定采用浅拷贝还是深拷贝,一般情况下应该尽量执行浅拷贝。
- 如果你所写的对象需要深拷贝,那么可考虑新增一个专门执行深拷贝的方法。