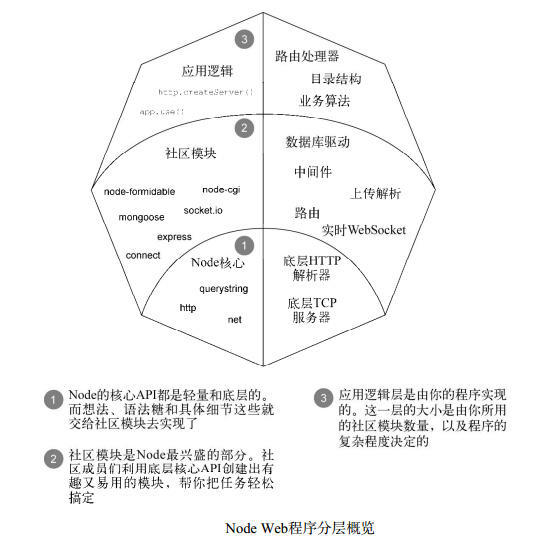
一、HTTP 服务器的基础知识
Node 的 http 模块:C 编写、底层、简单、灵活、高效。
Node 的策略是提供小而强的网络 API,像会话(Session)这种高级概念以及 HTTP cookies 这样的基础组件都没有包括在 Node 的内核之中。那些都要由第三方模块提供。
1. Node 如何向开发者呈现 HTTP 请求
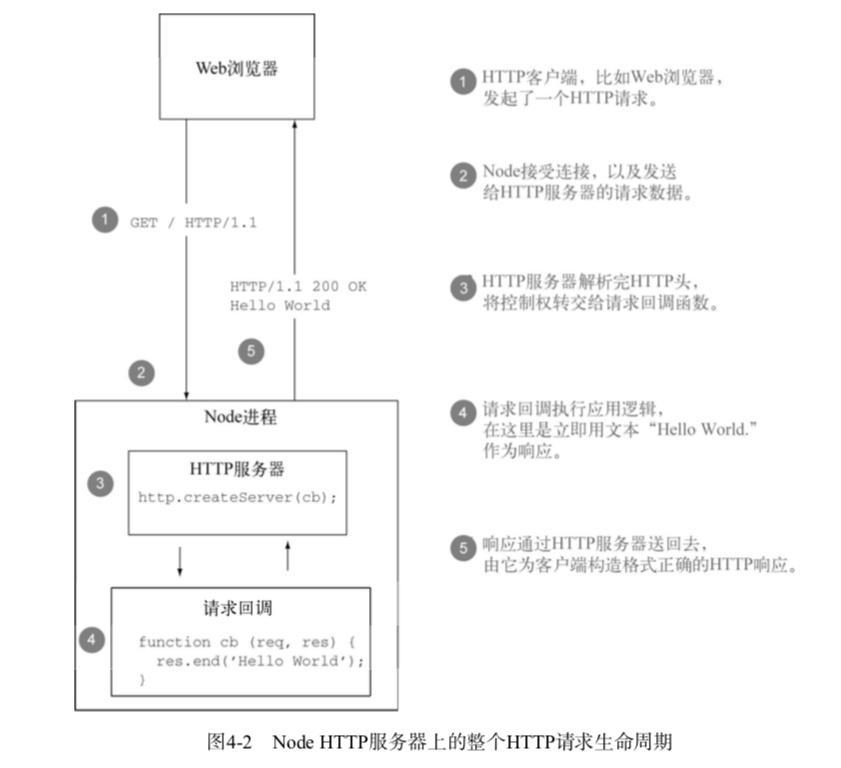
Node 服务器收到 HTTP 请求之后:
- 解析 HTTP 请求头(HTTP Head);
- 触发回调函数(function (req, res) {…} );
- 解析 HTTP 请求体(HTTP Body);
- 执行应用逻辑;
- 调用
res.end()结束响应;
2. 一个用 “Hello World” 做响应的 HTTP 服务器
// http 模块提供了HTTP服务器和客户端接口。
const http = require('http');
// http.createServer():创建HTTP服务器,服务器每次收到HTTP请求后都会调用它的回调函数
var server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
// res.write():将响应数据写到socket中
res.write('Hello World');
// res.end():结束响应
res.end();
// res.write() 和 res.end() 可以合并缩写:
// res.end('Hello World');
});
// 绑定监听端口
server.listen(3000);3. 读取、设定响应头
Node 中修改 HTTP 响应头的方法:
res.setHeader(field, value)res.getHeader(field, value)res.removeHeader(field)
添加和移除响应头的顺序可以随意,但一定要在调用 res.write() 或 res.end() 之前。
示例,使用 res.setHeader():
var body = 'Hello World';
res.setHeader('Content-Length', Buffer.byteLength(body));
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.end(body); 4. 设定 HTTP 响应的状态码
响应状态码需要设定 res.statusCode 属性。在程序响应期间可以随时给这个属性赋值,只要是在第一次调用 res.write() 或 res.end() 之前就行。
res.statusCode 默认的响应状态码是 200 OK。
var body = 'Hello World';
res.setHeader('Content-Length', Buffer.byteLength(body));
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.statusCode = 302;
res.end(body);
// 以上可以简写如下:
const body = 'Hello World';
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Length': Buffer.byteLength(body),
'Content-Type': 'text/plain'
});
res.end();参考:Wikiwand:HTTP 状态码
| HTTP 状态码 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1xx | 消息 |
| 2xx | 成功 |
| 3xx | 重定向 |
| 4xx | 客户端错误 |
| 5xx | 服务器错误 |
二、构建 RESTful Web 服务
创建标准的 REST 服务器需要实现四个 HTTP 谓词,每个谓词会覆盖一个待办事项清单的操作任务:
| HTTP Method | Description |
|---|---|
| POST | 增,向待办事项清单中添加事项 |
| GET | 查,显示当前事项列表,或者显示某一事项的详情; |
| DELETE | 删,从待办事项清单中移除事项; |
| PUT | 改,修改已有事项 |
1. 用 POST 请求创建资源
当 Node 的 HTTP 解析器读入并解析请求数据时,它会将数据做成 data 事件的形式,把解析好的数据块放入其中,等待程序处理:
const http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
// 数据块默认是 Buffer 对象
// 将流编码设定为utf8,这样data事件会给出字符串
req.setEncoding('utf8');
// 1. 只要读入了新的数据块,就会触发 data 事件。
req.on('data', function (chunk) {
console.log('parsed', chunk);
});
// 2. 数据全部读取完之后,触发 end 事件。
req.on('end', function() {
console.log('done parsing');
res.end();
})
})在 Node 中,可以通过检查 req.method 属性查看用的是哪个 HTTP 方法 (谓词)。
示例:POST 请求字符串缓存:
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');
var items = []; // 用一个JS数组存放数据
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
switch (req.method) {
case 'POST':
var item = ''; // 进来的字符串缓存
req.setEncoding('utf8'); // 将进来的 data 事件编码为 utf8
req.on('data', function (chunk) {
item += chunk;
});
req.on('end', function () {
items.push(item); // 将完整的事项压入数组
res.end('OK\n');
});
break;
default:
break;
}
})
server.listen(3000);2. 用 GET 请求获取资源
switch 中添加如下分支:
case 'GET':
items.forEach(function (item, i) {
res.write(i + ') ' + item + '\n');
})
res.end;
break;测试:
cURL是一个强大的命令行 HTTP 客户端,可以用来向目标服务器发送请求。
# -d 表示请求方法为 POST
$ curl -d 'buy groceries' http://localhost:3000
OK
$ curl -d 'buy node in action' http://localhost:3000
OK
# GET 是默认的方法
$ curl http://localhost:3000
0) buy groceries
1) buy node in action设定 Content-Length 头
在响应中设置 Content-Length 可以提高响应速度。
设定 Content-Length 域会隐含禁用 Node 的块编码,因为要传输的数据更少,所以能提升性能。
经过优化的 GET 处理如下:
case 'GET':
var body = items.map(function (item, i) {
return i + ') ' + item;
}).join('\n');
res.setHeader('Content-Length', Buffer.byteLength(body)); // ⚠️
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain; charset="utf-8"');
res.end(body);
break;⚠️
Buffer.byteLength()
你可能想用
body.length的值设定 Content-Length,但 Content-Length 的值应该是字节长度,不是字符长度,并且如果字符串中有多字节字符,两者的长度是不一样的。为了规避这个问题,Node 提供了一个Buffer.byteLength()方法。# Node REPL 测试 ☁ ~ [master] ⚡ node > 'etc张三'.length 5 > Buffer.byteLength('etc张三') 9
Node REPL 环境
Node 跟很多其他语言一样,提供了一个 REPL (读取 - 计算 - 输出 - 循环) 环境,在命令行中不带任何参数运行 node 就可以进入这个环境。用 REPL 可以编写代码片段,每条语句写好并执行后马上就能得到结果。对于学习编程语言、运行简单的测试,甚至是调试都很有帮助。
3. 用 DELETE 请求移除资源
req.url 属性中包含了客户端请求的 URL,根据请求的不同,其中可能包含几个组成部分。
$ node
> require('url').parse('http://localhost:3000/v1?key=value')
Url {
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
host: 'localhost:3000',
port: '3000',
hostname: 'localhost',
hash: null,
search: '?key=value',
query: 'key=value',
pathname: '/v1',
path: '/v1?key=value', # 请求路径
href: 'http://localhost:3000/v1?key=value' }DELETE 请求处理代码片段:
case 'DELETE':
var path = url.parse(req.url).pathname;
// pathname是字符串,需要将字符串转换为数字
// String.slice(),提取字符串的第一个字符串
// parseInt(),JavaScript 的全局函数,解析一个字符串,返回整数。
// 10 表示字符串基数,十进制。
var i = parseInt(path.slice(1), 10);
if (isNaN(i)) { // 检查数字是否有效
res.statusCode = 400;
res.end('Invalid item id');
} else if (!items[i]) { // 确保请求的索引存在
res.statusCode = 400;
res.end('Item not found');
} else {
items.splice(i, 1); // 删除请求的事项
res.end('OK\n');
}
break;三、提供静态文件服务
静态文件(CSS、JavaScript、图片)服务器。
fs(文件系统)模块,是提供静态服务的必备模块。
1. 创建一个静态文件服务器
每个静态文件服务器都有个根目录,也就是提供文件服务的基础目录。
const http = require('http');
const parse = require('url').parse;
const join = require('path').join;
const fs = require('fs');
var root = __dirname; // 静态文件服务器的根目录
/*
* url.pathname = /index.html
* root = /var/www/example.com/public
*
* path.join() => /var/www/example.com/public/index.html
*/
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
var url = parse(req.url);
var path = join(root, url.pathname); // 构造绝对路径
var stream = fs.createReadStream(path); // fs.ReadStream
stream.on('data', function (chunk) {
res.write(chunk); // 将文件数据写入到响应中
})
stream.on('end', function () {
res.end(); // 文件写完后结束响应
})
})
server.listen(3000);⚠️
目录遍历攻击
生产环境中,应该全面地检查输入的有效性,以防用户通过目录遍历攻击访问到你本来不想开放给他们的那部分内容。
用 Stream.pipe () 优化数据传输
管道和水管
管道可以让来自源头(即 ReadableStream)的数据,流到某个目的地(即 WritableStream)。
用
pipe()方法连接管道。ReadableStream.pipe(WritableStream);
读取一个文件(ReadableStream)并把其中的内容写到另一个文件中(WritableStream)用的就是管道:
var readStream = fs.createReadStream('./original.txt'); var writeStream = fs. createWriteStream('./copy.txt'); readStream.pipe(writeStream);所有 ReadableStream 都能接入任何一个 WritableStream。比如 HTTP 请求 (req) 对象就是 ReadableStream,你可以让其中的内容流动到文件中:
req.pipe(fs.createWriteStream('./req-body.txt'));
用 pipe () 简化服务器端代码:
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
var url = parse(req.url);
var path = join(root, url.pathname); // 构造绝对路径
var stream = fs.createReadStream(path); // fs.ReadStream
stream.pipe(res); // res.end() 会在 stream.pipe() 内部调用
})2. 处理服务器错误
如何让 Node 服务器更加健壮?
默认情况下,如果没有设置监听器,error 事件会被抛出。也就是说如果你不监听这些错误,那它们就会搞垮你的服务器。
...
stream.pipe(res);
stream.on('error', function (err) { // 注册error事件处理器
res.statusCode = 500;
res.end('Internal Server Error');
});
...3. 用 fs.stat () 实现先发制人的错误处理
fs.stat() 用于获取文件相关信息。
检查文件是否存在,并在响应中提供 Content-Length
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
var url = parse(req.url);
var path = join(root, url.pathname); // 构造绝对路径
fs.stat(path, function (err, stat) { // 检查文件是否存在
if (err) {
if ('ENOENT' == err.code) {
res.statusCode = 404;
res.end('Not Found');
} else { // 其他错误
res.statusCode = 500;
res.end('Internal Server Error');
}
} else {
// 用 stat 对象的属性设置 Content-Length
res.setHeader('Content-Length', stat.size);
var stream = fs.createReadStream(path); // fs.ReadStream
stream.pipe(res); // res.end() 会在 stream.pipe() 内部调用
stream.on('error', function (err) {
res.statusCode = 500;
res.end('Internal Server Error');
});
}
});
})💡💡💡
不推荐在调用
fs.open(),fs.readFile()orfs.writeFile()前通过使用fs.stat()来检查某个文件是否存在。对于这种情况,开发者应当通过直接 open/read/write 文件并检测产生的异常来判断文件是否可用。如果不需要操作文件只是想获取文件是否可用,推荐使用
fs.access()。
四、从表单中接受用户输入
Node 不会帮你承担处理表单的工作 (比如验证或文件上传),它只能把请求 body 数据交给你。尽管这看起来不太方便,但 Node 一贯的宗旨是提供简单高效的底层 API,把其他机会留给了第三方框架。
| 表单提交的 Content-Type 值 | Description |
|---|---|
| application/x-www-form-urlencoded | HTML 表单默认值 |
| multipart/form-data | 表单中含有文件或非 ASCII 或二进制数据时使用 |
1. 处理提交的表单域
支持 GET 和 POST 的 HTTP 服务器:
const http = require('http');
const qs = require('querystring');
var items = [];
var server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
if ('/' == req.url) {
switch (req.method) {
case 'GET':
show(res);
break;
case 'POST':
add(req, res);
break;
default:
badRequest(res);
}
} else {
notFound(res);
}
});
server.listen(3000);
function show(res) {
// 用拼接字符串的方法生成 HTML
var html = '<html><head><title>Todo List</title></head><body>'
+ '<h1>Todo List</h1>'
+ '<ul>'
+ items.map(function (item) {
return '<li>' + item + '</li>'
}).join(' ')
+ '</ul>'
+ '<form method="post" action="/">'
+ '<p><input type="text" name="item" /></p>'
+ '<p><input type="submit" value="Add Item" />></p>'
+ '</form></body></html>';
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.setHeader('Content-Length', Buffer.byteLength(html));
res.end(html);
}
function add(params) {
var body = '';
req.setEncoding('utf8');
req.on('data', function (chunk) {
// 把data事件的数据块拼接到一起形成完整的请求body字符串。
body += chunk;
});
req.on('end', function () {
var obj = qs.parse(body);
items.push(obj.item);
show(res);
});
}
// 404 Not Found
function notFound(res) {
res.statusCode = 404;
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.end('Not Found');
}
// 400 Bad Requests
function badRequest(res) {
const body = 'Bad Request';
res.writeHead(400, {
'Content-Length': Buffer.byteLength(body),
'Content-Type': 'text/plain'
});
res.end(body);
}2. 用 formidable 处理上传的文件
实现 Web 中的文件上传功能。
:hexoPostRenderEscape–><!--上传文件时,表单的 enctype 属性需要设置为 multipart/form-data-->
<form method=“POST“ action=“/“ enctype=“multipart/form-data“>
<p><input type=“text“ name=“name“ /></p>
<p><input type=“text“ name=“file“ /></p>
<p><input type=“submit“ value=“Upload“></p>
</form>
第三方模块:npm:formmidable,formidable 的流式解析器是处理文件上传的绝佳选择,也就是说它能随着数据块的上传接收它们,解析它们,并吐出特定的部分。这种方式不仅快速,还不会因为需要大量缓冲而导致内存膨胀,即便像视频这种大型文件,也不会把进程压垮。
const http = require('http');
const formidable = require('formidable');
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
switch (req.method) {
case 'GET':
show(req, res);
break;
case 'POST':
upload(req, res);
break;
}
});
server.listen(3000);
// GET
function show(res) {
// 带有文件上传控件的 HTML 表单
var html = ' '
+ '<form method="post" action="/" enctype="multipart/form-data">'
+ '<p><input type="text" name="name" /></p>'
+ '<p><input type="file" name="file" /></p>'
+ '<p><input type="submit" value="Upload" /></p>'
+ '</form>';
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.setHeader('Content-Length', Buffer.byteLength(html));
res.end(html);
}
function upload(req, res) {
if (!isFormData(req)) {
res.statusCode = 400;
res.end('Bad Request: expecting multipart/form-data');
return;
}
var form = new formidable.IncomingForm();
// // 收完输入域后会发出 field 事件
// // 每当收到字段 / 值对时发出。
// form.on('field', function (name, value) {
// console.log(name);
// console.log(value);
// });
// // 在收到文件并处理好后会发出 file 事件
// // 文件上传完成后发出了file事件
// // 每当收到字段 / 文件对时发出。
// form.on('file', function (name, file) {
// console.log(name);
// console.log(file);
// });
// form.on('end', function () {
// res.end('upload complete');
// });
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
console.log(fields);
console.log(files);
res.end('upload complete');
});
}
// 用String.indexOf()方法检查请求头中的Content-Type字段, 断言它的值是以multipart/form-data开头的。
function isFormData(req) {
var type = req.headers['content-type'] || '';
return 0 == type.indexOf('multipart/form-data');
}3. 计算上传进度
Formidable 的 progress 事件能给出收到的字节数,以及期望收到的字节数。我们可以借助这个做出一个进度条。
form.on('progress', function(bytesReceived, bytesExpected) {
var percent = Math.floor(bytesReceived / bytesExpected * 100);
console.log(percent);
});接下来,把这个进度传回到用户的浏览器中,可以使用 WebSocket 协议或者 Socket.IO 这样的实时模块。
五、用 HTTPS 加强程序的安全性
开发环境中,生成自签名证书用于测试:
# 使用 OpenSSL 生成私钥
$ openssl genrsa 2048 > key.pem
# 使用私钥创建证书
$ openssl req -x509 -new -key key.pem > key-cert.pemHTTPS 服务器配置项:
'use strict';
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
// 作为配置项的密钥和证书
var options = {
key: fs.readFileSync('./key.pem'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('./key-cert.pem')
};
// https 和 http 模块的API几乎一样
https.createServer(options, function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end('Hello World');
}).listen(3000);